JavaScript — Behavior & Logic
Core language, DOM APIs, async programming, modules, and storage.
Introduction to JavaScript
JavaScript (JS) is the programming language of the web. It adds logic and interactivity to otherwise static HTML & CSS pages. Nearly every modern website uses JS for tasks such as:
- Validating form input before sending to the server.
- Creating dynamic UI elements like dropdowns, sliders, and tabs.
- Communicating with servers using AJAX or Fetch APIs.
- Building entire applications in the browser (SPAs with React, Angular, Vue).
Tip: Learn the difference between
var, let, and const. They control variable scope.Control Flow Example
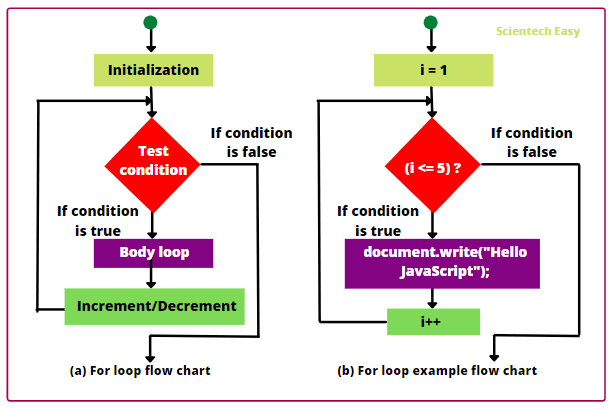
JavaScript supports conditionals (if, else) and loops (for, while) for decision making and repetition.
for (let i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
console.log("Step " + i);
}
Functions
Functions are reusable blocks of code. They can take parameters and return values.
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(add(3, 5)); // 8
DOM Manipulation Example
Use JavaScript to change page content dynamically.
document.getElementById("title").textContent = "Updated with JS";Original Title
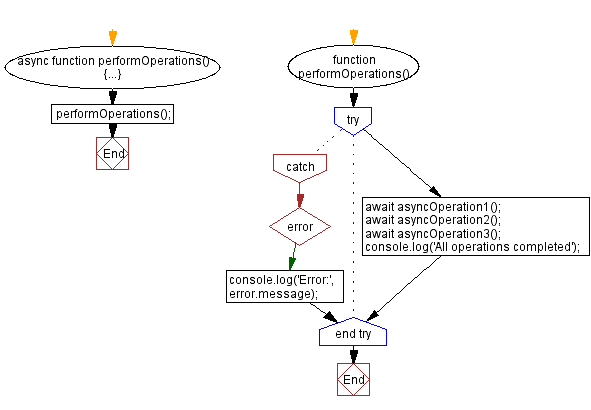
Async Example with Image
You can fetch and display data (or images) without reloading the page.
async function loadImage(){
const res = await fetch("https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random");
const data = await res.json();
document.getElementById("dog").src = data.message;
}
Data Types, Variables, Functions
let n = 1, s = "hi", ok = true, arr = [1,2], obj = {x:1};
const add = (a,b) => a + b;DOM & Events
document.getElementById('btn').addEventListener('click', () => {
alert('Clicked!');
});Fetch & Async/Await
async function getPosts(){
const res = await fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts?_limit=3');
return res.json();
}Local Storage
localStorage.setItem('theme','dark');
console.log(localStorage.getItem('theme'));Try It Yourself (HTML + CSS + JS)